Data Analysis: Why Only 1 in 5 Companies Focus on Fixing Cyberattacks
Business leaders are rethinking cybersecurity. This deep dive reveals where companies are actually investing, and what they are leaving behind.
Cyber threats are getting smarter and so are the companies fighting them. But where exactly are business leaders putting their cybersecurity investment in 2025? This post breaks down the top five investment priorities, from data protection to employee training, and reveals a surprising mindset in cybersecurity investment. If you want to understand what today’s smartest organizations are doing differently to stay safe online, keep reading.
Cybersecurity Investment Priorities for Business Leaders Worldwide
The security of information systems has become a non-negotiable priority for organizations across the globe. The complexity and volume of cyber threats have grown exponentially. Consequently, business leaders are compelled to reevaluate their cybersecurity strategies and prioritize investments that enhance resilience, protect data, and maintain stakeholder trust.
This post discusses recent trends in cybersecurity investment priorities of business leaders worldwide, based on a comprehensive analysis of a recent global survey.
It explores why certain cybersecurity areas receive greater attention, the implications of these investment decisions, and the strategic outlook for cybersecurity.
1. Data Protection or Data Trust (48%)
Leading the list of cybersecurity investment priorities is data protection or data trust, with 48% of respondents identifying this as their foremost concern.
This overwhelming focus demonstrates the centrality of data in today’s digital economy. Organizations across industries are collecting, storing, and processing vast quantities of data, from customer information and financial records to intellectual property and operational intelligence.
Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of this data is critical not only for compliance but also for competitive advantage.
The emphasis on data trust is fuelled by stringent regulatory frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, and numerous similar laws worldwide.
These regulations mandate rigorous data protection measures and impose significant penalties for non-compliance, making data security a top boardroom issue.
Moreover, consumer expectations around data privacy have evolved. In a digital marketplace where trust is currency, organizations that demonstrate a commitment to protecting user data are more likely to foster loyalty and brand advocacy.
High-profile data breaches in recent years have further amplified public scrutiny and regulatory pressure, prompting companies to invest heavily in secure data storage, encryption technologies, access control mechanisms, and privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs).
2. Modernization of Technology, Including Cyber Infrastructure (43%)
Closely following data protection is the modernization of technology and cyber infrastructure, cited by 43% of respondents. This priority reflects a recognition that legacy systems are often ill-equipped to withstand modern cyber threats. Aging infrastructure can harbor vulnerabilities that are difficult to patch or mitigate, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Investments in modern cybersecurity infrastructure encompass a broad spectrum of technologies, including cloud computing, zero trust architectures, secure access service edge (SASE) frameworks, and advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems. These technologies not only enhance the robustness of organizational defenses but also enable greater flexibility, scalability, and visibility across IT environments.
The transition to remote and hybrid work models has also accelerated the need for infrastructure modernization. With employees accessing corporate networks from various locations and devices, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient. Organizations must adopt more dynamic and context-aware approaches to securing endpoints, applications, and data.
In addition, the rise of digital supply chains, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and smart systems necessitates an integrated and adaptive security framework. Modern cyber infrastructure enables real-time threat detection, automated incident response, and continuous monitoring, all of which are essential for maintaining a strong security posture.
3. Ongoing Security Training (34%)
Human error remains one of the most significant cybersecurity vulnerabilities. As such, 34% of business leaders prioritize ongoing security training for employees. This investment recognizes that even the most sophisticated technologies can be rendered ineffective if users lack awareness or inadvertently engage in risky behaviours.
Security training programs aim to cultivate a security-conscious culture within organizations. These initiatives typically cover topics such as phishing awareness, password hygiene, secure browsing practices, and incident reporting protocols. Regular training sessions, simulated phishing attacks, and gamified learning modules are among the tools used to reinforce key concepts and assess employee readiness.
The return on investment in security training is substantial. Studies have shown that well-trained employees are less likely to fall victim to social engineering attacks and more likely to detect and report suspicious activities. By empowering staff with the knowledge and skills to identify potential threats, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface.
Moreover, security training supports compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Frameworks such as ISO/IEC 27001, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and various sector-specific guidelines emphasize the importance of personnel training as part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
4. Ongoing Improvements in Risk Posture Based on Cyber Roadmap (30%)
Thirty percent of respondents emphasize ongoing improvements in risk posture, guided by a structured cyber roadmap. This strategic focus reflects a shift from reactive to proactive cybersecurity management. Rather than waiting for incidents to occur, organizations are increasingly adopting a risk-based approach to identify, assess, and mitigate potential threats before they materialize.
A cyber roadmap outlines the organization’s long-term cybersecurity goals, the steps needed to achieve them, and the metrics for measuring progress. It typically includes initiatives such as risk assessments, vulnerability management, policy development, security architecture reviews, and investment planning.
Continuous improvement in risk posture involves regular updates to the roadmap based on threat intelligence, technological advancements, and changes in the business environment. This agile approach allows organizations to stay ahead of new threats and adapt to emerging challenges.
Additionally, a well-defined cyber roadmap facilitates cross-functional collaboration and executive alignment. By articulating cybersecurity objectives in business terms, security leaders can secure buy-in from stakeholders, justify budget allocations, and demonstrate the value of security investments.
5. Remediation in the Aftermath of Cyber Breaches or Intrusions (20%)
Interestingly, only 20% of business leaders prioritize remediation after cyber breaches or intrusions. While this may seem counterintuitive given the prevalence of cyberattacks, it reflects a broader strategic pivot toward prevention rather than response.
Remediation efforts typically involve activities such as forensic investigations, system restoration, legal and regulatory reporting, customer notification, and reputation management. While essential, these actions are often reactive and costly. As such, many organizations prefer to invest in preventive measures that reduce the likelihood and impact of breaches.
That said, the relatively low prioritization of remediation does not imply a disregard for incident response. On the contrary, mature cybersecurity programs integrate robust incident response plans, disaster recovery protocols, and business continuity strategies. These components are critical for minimizing downtime, preserving data integrity, and maintaining operational resilience during and after an attack.
The emphasis on prevention also aligns with the principles of cyber resilience, which advocate for a holistic approach to managing cyber risks. Resilient organizations not only defend against threats but also ensure they can recover swiftly and learn from incidents to enhance future preparedness.
Implications of Cybersecurity Investment Priorities
The investment patterns revealed in the survey have several important implications for businesses, policymakers, and cybersecurity professionals:
Moving from Reactive to Proactive Security: The data highlights a clear trend toward proactive security strategies that emphasize prevention, resilience, and continuous improvement.
Emphasis on Trust and Compliance: The prioritization of data protection reflects the growing importance of digital trust and regulatory compliance. Organizations must not only secure their systems but also demonstrate transparency and accountability in their data practices.
Workforce as the First Line of Defense: Investing in security training reinforces the recognition that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility. Engaging and educating employees is essential for building a security-aware culture.
Need for Agile Infrastructure: Modernizing cyber infrastructure is no longer optional. Organizations must embrace flexible, scalable, and integrated technologies to support secure digital transformation.
Balancing Prevention and Response: While prevention is rightly prioritized, effective remediation capabilities remain vital. A balanced approach that includes robust incident response and recovery plans is essential for comprehensive cyber risk management.
Cybersecurity has emerged as a strategic priority for business leaders worldwide. As digital threats become more sophisticated and pervasive, organizations must make informed decisions about where to allocate resources for maximum impact.
The insights from this analysis provide a roadmap for aligning cybersecurity investments with organizational goals, regulatory requirements, and stakeholder expectations.
Data protection, technology modernization, security training, risk posture improvements, and breach remediation each play a vital role in a holistic cybersecurity strategy.






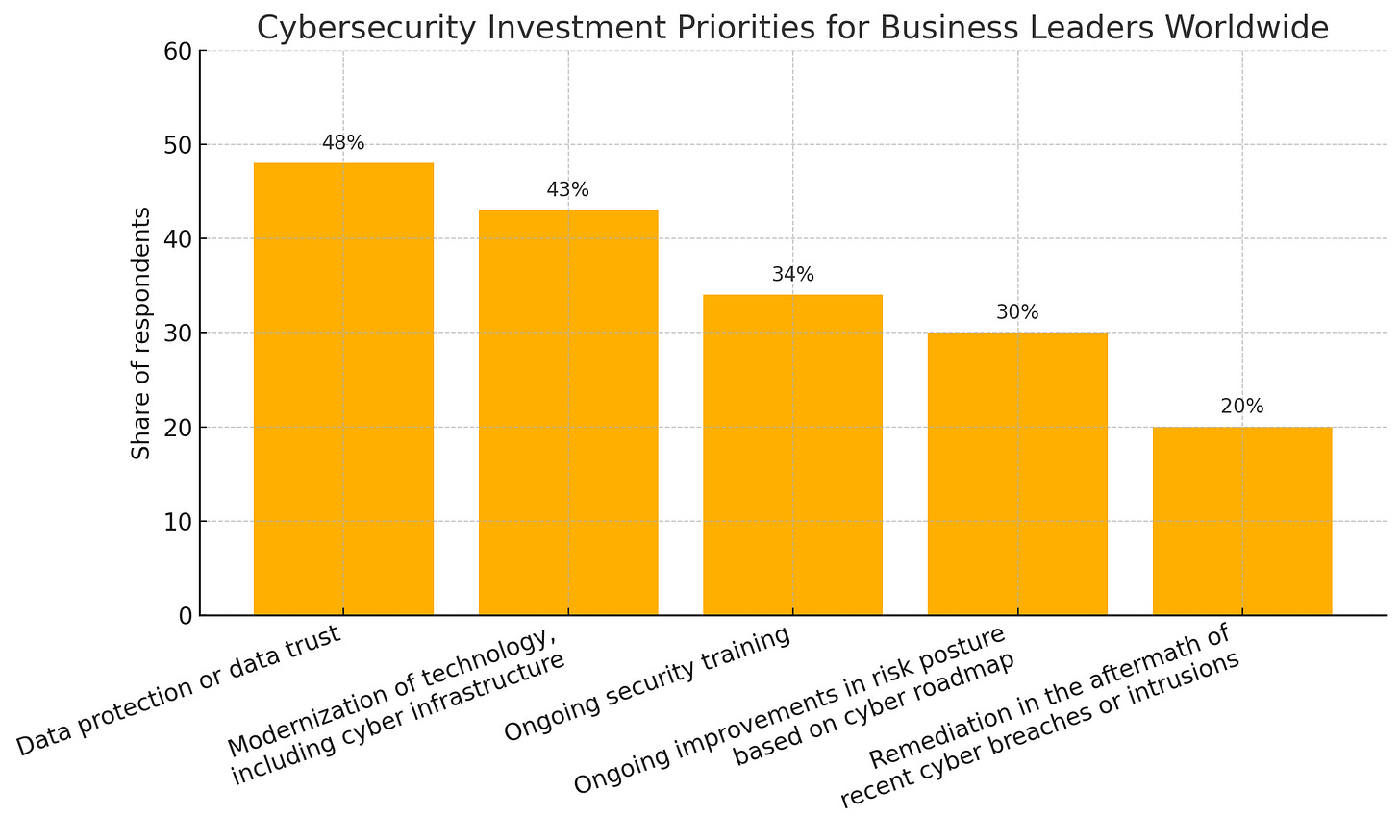
In 2025, nearly half of business leaders are putting their cybersecurity budget into data protection and trust. Regulations like GDPR and CCPA mandate tight controls on how personal data is handled. Ignoring this can lead to lawsuits, fines, and brand damage. It is worth prioritizing encryption, access control, and secure storage.